infertility
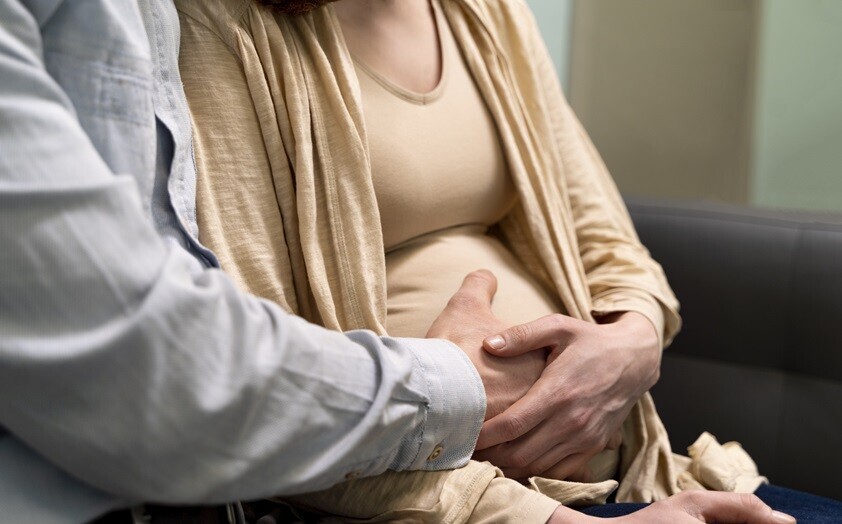
A Concise Overview of the Altruistic Surrogacy Treatment Process
Altruistic surrogacy, a selfless act of carrying a child for intended parents without financial compensation, is a journey bound by empathy and trust. Here is a brief guide to understanding the altruistic surrogacy treatment process:
- Initial Consultation: The process typically begins with an initial consultation with a fertility specialist or a surrogacy center. During this consultation, intended parents discuss their medical history, fertility concerns, and the desire for surrogacy. The medical team evaluates their suitability for surrogacy and provides an overview of the process.
- Matching Process: Once the decision for surrogacy is made, intended parents and the surrogate mother undergo a matching process. This involves compatibility assessments based on personal preferences, medical history, and legal considerations. The goal is to ensure a harmonious partnership between the intended parents and the surrogate.
- Medical Evaluation: Both the intended parents and the surrogate mother undergo comprehensive medical evaluations to assess their reproductive health. This includes physical examinations, hormone tests, and screenings for infectious diseases. The results inform the medical team’s recommendations for the surrogacy treatment plan.
- Legal Formalities: Legal agreements are drafted to outline the rights, responsibilities, and expectations of all parties involved in the surrogacy arrangement. These contracts address issues such as parental rights, financial arrangements, and potential medical complications. It’s crucial to involve legal experts specializing in surrogacy laws to ensure legal clarity and protection for all parties.
- Medical Procedures: The surrogacy treatment typically involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), where eggs from the intended mother or a donor are fertilized with sperm from the intended father or a donor in a laboratory setting. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the surrogate mother’s uterus through a minimally invasive procedure. Hormonal medications may be prescribed to synchronize the menstrual cycles of the intended mother or donor and the surrogate for optimal timing.
- Pregnancy and Support: Once the embryo transfer is successful, the surrogate mother undergoes regular prenatal care to monitor the pregnancy’s progress. Intended parents provide emotional support and may accompany the surrogate to medical appointments. Open communication and mutual respect are essential throughout the pregnancy journey.
- Birth and Parental Rights: When the surrogate mother gives birth, parental rights are established according to the legal agreements in place. In altruistic surrogacy, the intended parents are recognized as the legal parents from birth, and the surrogate relinquishes any parental rights. This process may vary depending on the jurisdiction’s surrogacy laws and the specifics of the legal agreement.
- Postpartum Support: After the birth, intended parents and the surrogate mother may require postpartum support to navigate the emotional transition. Counseling services and support groups are available to address any lingering concerns or feelings and facilitate a smooth transition for all parties involved.
Altruistic surrogacy is a deeply meaningful and rewarding journey for both intended parents and surrogate mothers. With proper medical guidance, legal support, and emotional care, it offers hope and the opportunity to fulfill the dream of parenthood.
admin
0
Tags :